
What is the Red Sea Conflict and its Impact on Global Trade?
The global trade landscape has shown signs of stabilization following the impact of the pandemic. However, it’s currently facing significant disruptions due to the ongoing attacks by Houthi rebels in the Red Sea. This geopolitical development has introduced a new element of uncertainty and complexity, impacting international commerce and supply chain dynamics.
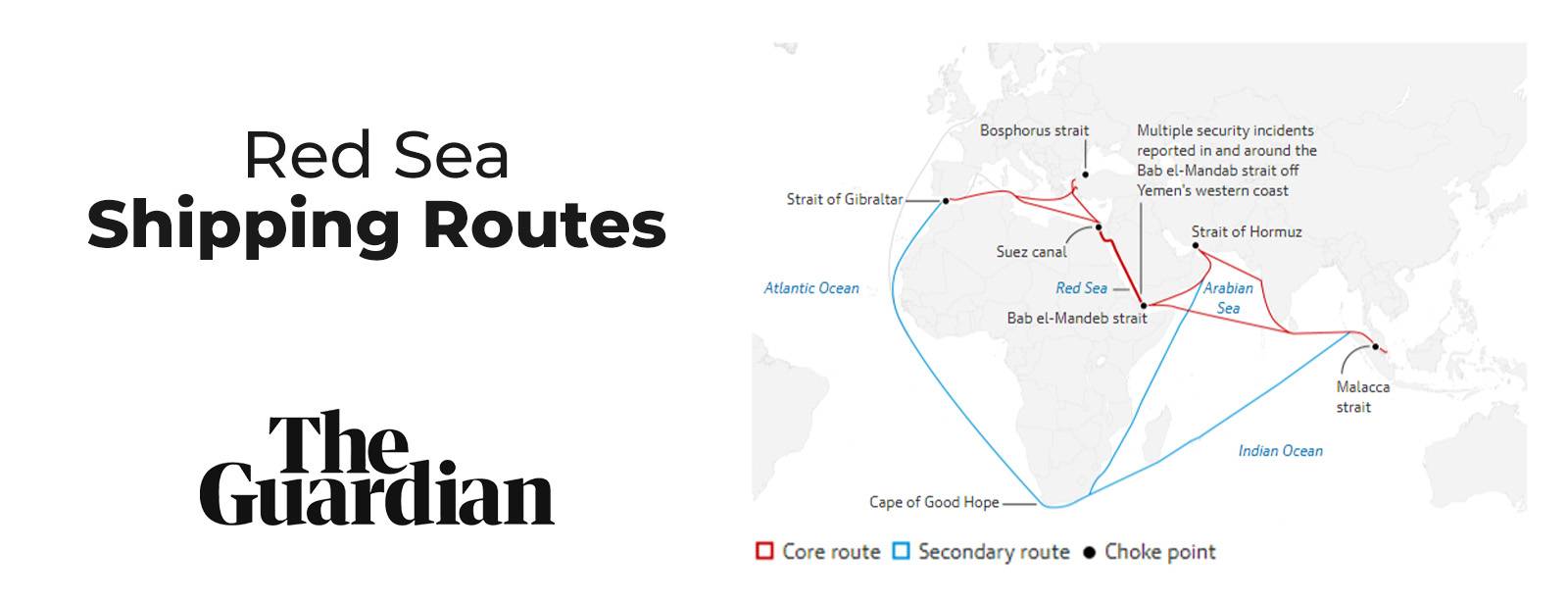
The situation demands careful monitoring and analysis as stakeholders navigate the evolving challenges posed by these disruptions in the vital maritime trade routes of the Red Sea.
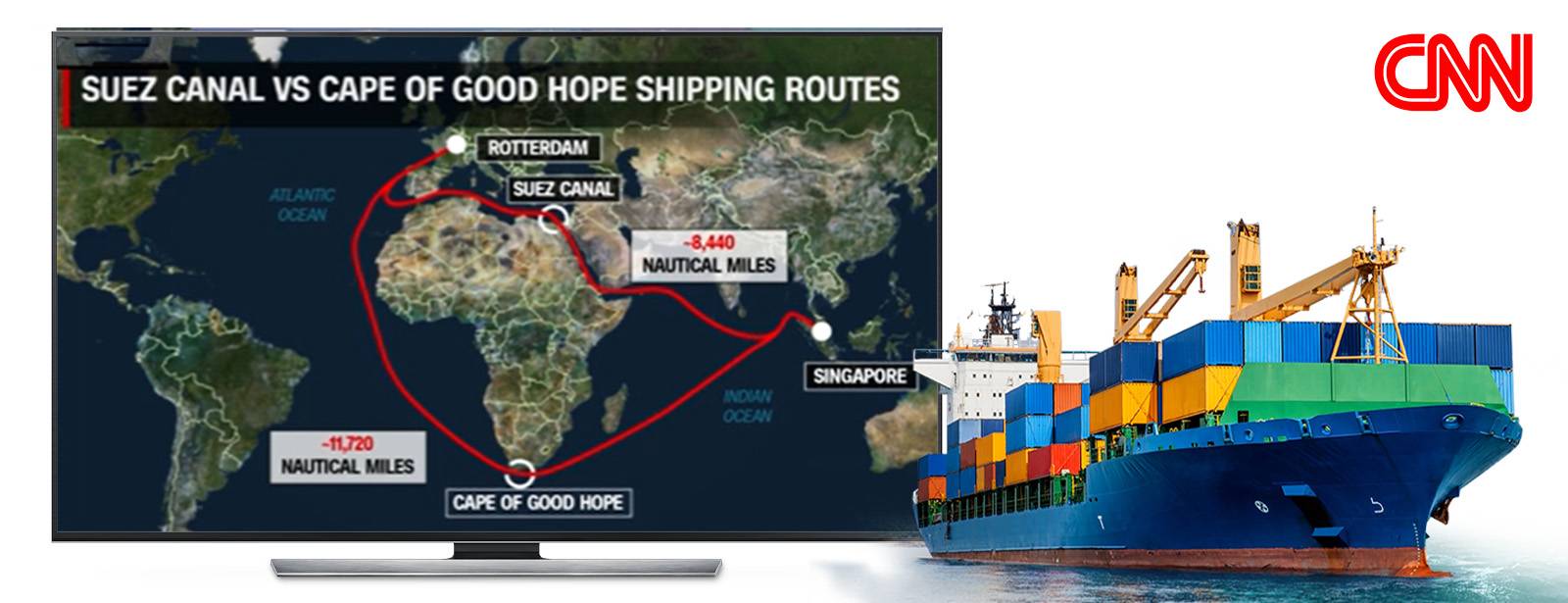
What’s the on-ground reality at the Red Sea?
Ever since the war broke out between Israel and Hamas back in October 2023, there have been several tense moments for global trade. And with Israel’s bombardment of Gaza, Iran-backed Houthi rebels in Yemen have significantly stepped up a campaign of attacks against commercial vessels. These attacks mainly focused on the Bab-el-Mandeb strait between the Arabian peninsula and the Horn of Africa. Last week saw a ship owned by Maersk being attacked which led the shipping company to pause all cargo movements.
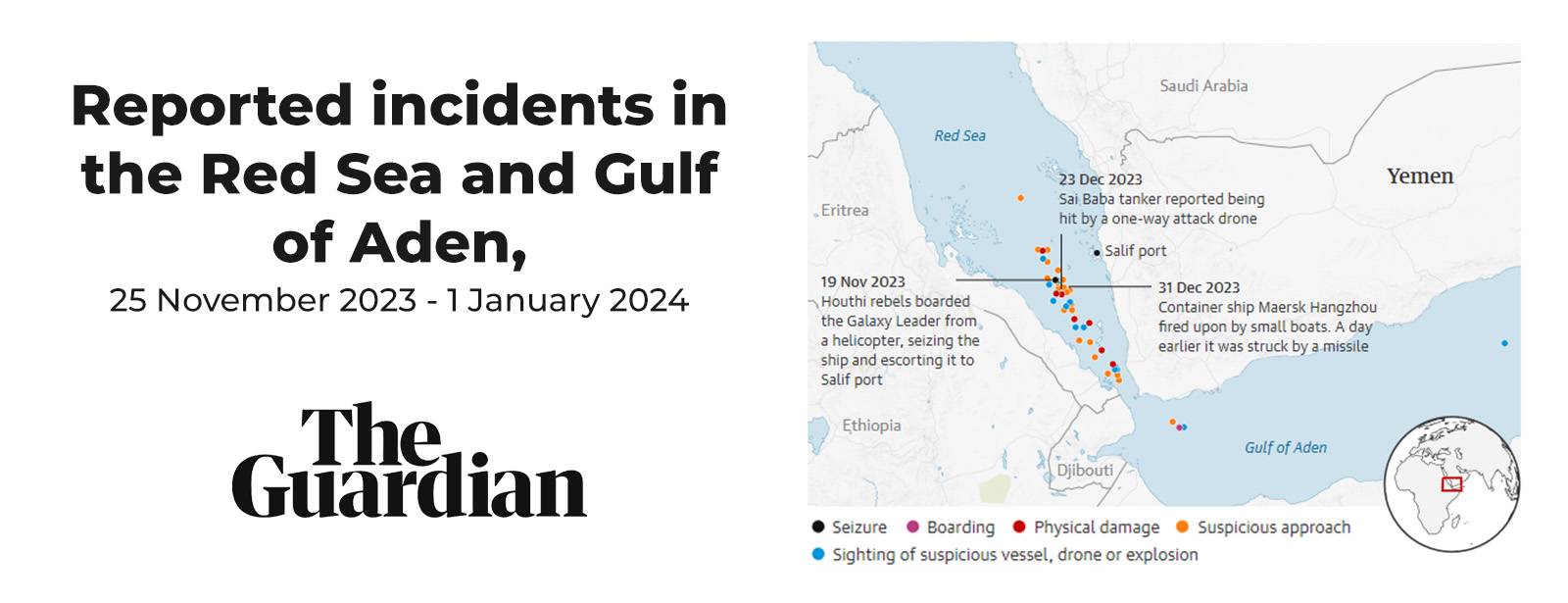
What’s the significance of the Red Sea trade route?
The Suez Canal is like a super important waterway that helps ships from Asia reach other places in the world. It handles 12% of global trade. It’s like a shortcut that saves a lot of time for ships carrying things like toys, clothes, and even oil. Imagine it as a big road for ships; without it, it would take much longer for these ships to deliver their stuff. So, when this route gets blocked or disrupted, it can affect the delivery of things all around the globe.

Are there no alternative routes for the Red Sea problem?
The alternate route goes around the Cape of Good Hope (Africa) which adds about 3,000-3,500 nautical miles (6,000km). This adds roughly 10 days of journey time connecting between Europe and Asia.


Which ports will be the most impacted?

As per reports, due to the increased shipping times, ports in the UK and major European hubs like Rotterdam, Antwerp, and Hamburg would be impacted.
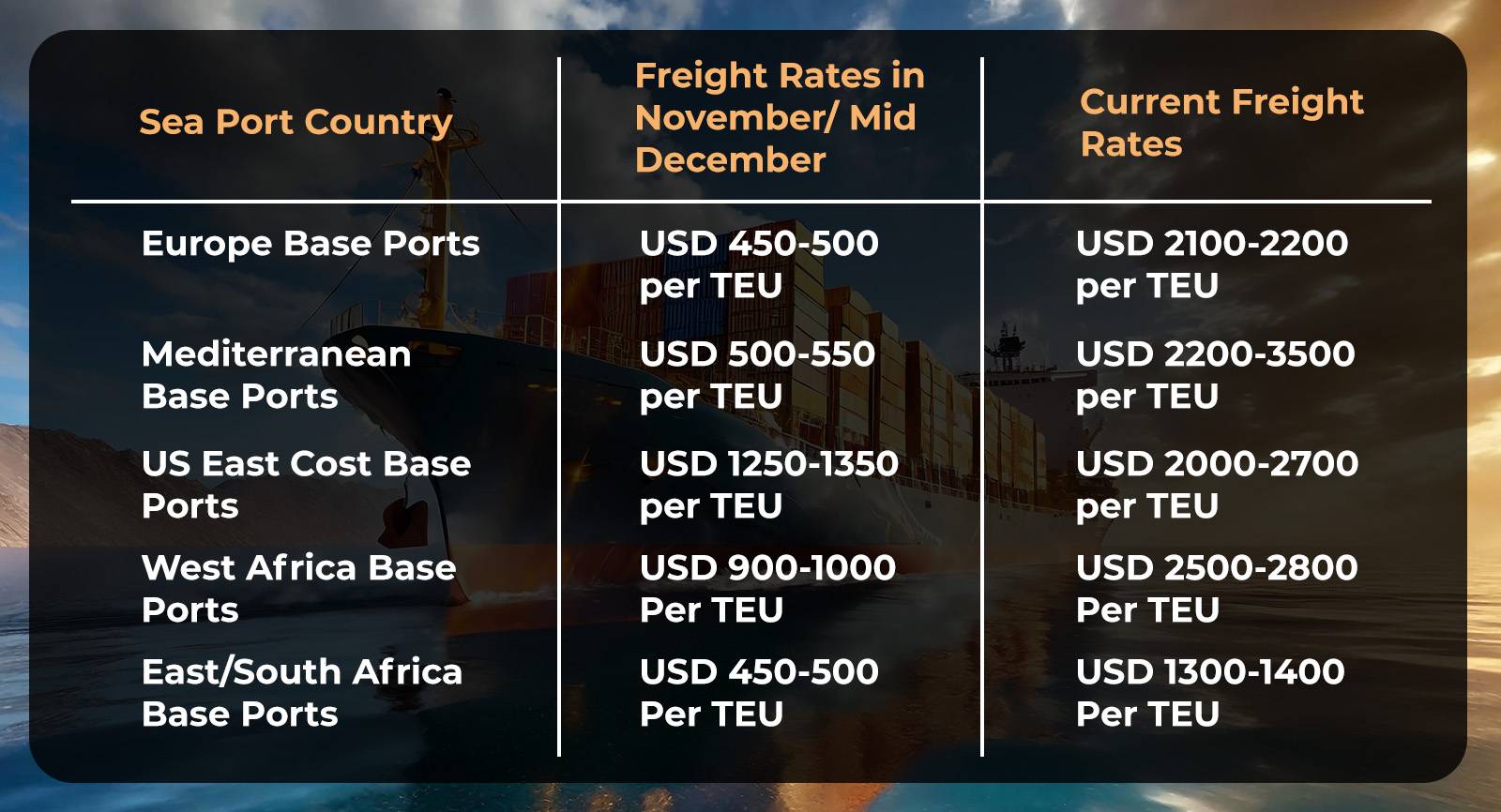
What does this mean for the shipping industry?
1. Due to ships being redirected, shipping fuel costs will rise by $1m for every round trip between Europe and Asia.
2. Since routes of Petroleum products like diesel and jet fuel are being diverted, some countries might face shortages.
3. Consumer goods like food and clothing will see delays in shipments.
4. The only positive is that crude oil prices have stayed relatively stable thus shippers will not have to shell extra.


Will this event have the same impact as the Suez Canal block in 2021?
As per industry experts, the Red Sea conflict will have a lesser impact on the global economy than the Suez Canal block in 2021.
This is because, in 2021 the world was getting back to its feet and consumers had started spending after the pandemic null. The supply chain then could not handle the consumer demands as demands exceed supply.

However, at present there is no such consumer demand. Also, due to slower economic growth and the rising risk of recession in the US, the UK and European regions have significantly reduced world trade volumes.
Although, the question remains about how the shipping industry will handle the annual surge of exports before the Lunar New Year.

Are you looking for software to get help for real-time visibility and improving customer experience? Look no further than LogiNext. Click on the red button below to set up a call with our expert.
124





@LogiNext