
Navigating the Chilled Maze: Demystifying Cold Supply Chain Logistics
In the modern world of global commerce, seamless delivery of goods to consumers requires the right mix of technology. Yet, when the products in question require strict temperature control throughout their journey, the complexity reaches a whole new level. The global cold supply chain logistics market is projected to grow from $242.39 billion in 2021 to $647.47 billion by 2028. Resulting in a CAGR of 15.1% in the forecast period.
What is a Cold Supply Chain?
A cold supply chain, also known as a cold chain, is a specialized logistics and distribution system. They are designed to maintain a specific temperature range throughout the entire journey of temperature-sensitive products. This type of supply chain is crucial for preserving the quality, safety, and efficacy of products that are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Some of the top industries that require a cold supply chain include pharmaceuticals, fresh food, vaccines, and certain chemicals.
The main objective of a cold chain is to ensure that products remain within their required temperature parameters from the point of production or manufacturing through transportation, storage, and distribution until they reach the end consumer. This typically involves keeping products at controlled low temperatures, which can range from freezing temperatures to refrigeration or even just maintaining a stable cool environment.
Key Components of a Cold Supply Chain
The cold supply chain plays a critical role in industries where product quality and safety are paramount, as it helps prevent spoilage, degradation, or potential health risks associated with temperature-sensitive goods. It ensures that consumers receive products that meet the necessary standards and specifications, making it essential for sectors like healthcare, food, and biotechnology.
How Does a Cold Chain Supplier Function? What is it?
A cold chain supplier, also known as a cold chain logistics provider, is responsible for ensuring that temperature-sensitive products are stored, transported, and distributed under controlled conditions. They invest in specialized equipment, infrastructure, and expertise to maintain the cold chain’s integrity, safeguarding products from temperature deviations.
Difference between a Cold Supply Chain vs. a Normal Supply Chain
| Cold Supply Chain | Normal Supply Chain |
| In a cold supply chain, maintaining a specific temperature range is critical. Products such as vaccines, fresh food, pharmaceuticals, and certain chemicals require precise temperature control to preserve their quality and safety. This often involves refrigeration or freezing conditions. | In a normal supply chain, temperature control is not a primary concern. The focus is on efficiently moving products from one point to another, and the majority of goods being transported do not require strict temperature regulation. |
| Temperature-sensitive products in a cold supply chain are highly susceptible to temperature fluctuations. Even slight deviations from the recommended temperature range can lead to product spoilage, reduced efficacy, or even safety risks. | Products in a normal supply chain are typically less sensitive to temperature variations. While some products may have specific storage requirements, they are not as vulnerable to temperature changes as those in a cold supply chain. |
| They require specialized infrastructure, equipment, and expertise. This includes refrigerated trucks, cold storage facilities, temperature monitoring devices, and trained personnel who understand the importance of temperature control. | Normal supply chains do not necessitate the same level of specialized equipment and knowledge. They focus on optimizing transportation and distribution processes rather than temperature regulation. |
| It is primarily used in industries where product quality and safety are paramount, such as pharmaceuticals, healthcare, biotechnology, and the food industry. Examples include transporting vaccines, fresh produce, and frozen foods. | Normal supply chains are prevalent in a wide range of industries, including retail, manufacturing, and general logistics. They deal with a broad spectrum of products with varying transportation and storage requirements. |
| They are more complex due to the need for continuous temperature monitoring, specialized handling, and strict adherence to temperature guidelines throughout the entire supply chain. | Normal supply chains are generally less complex, focusing on factors like cost efficiency, lead times, and inventory management. |
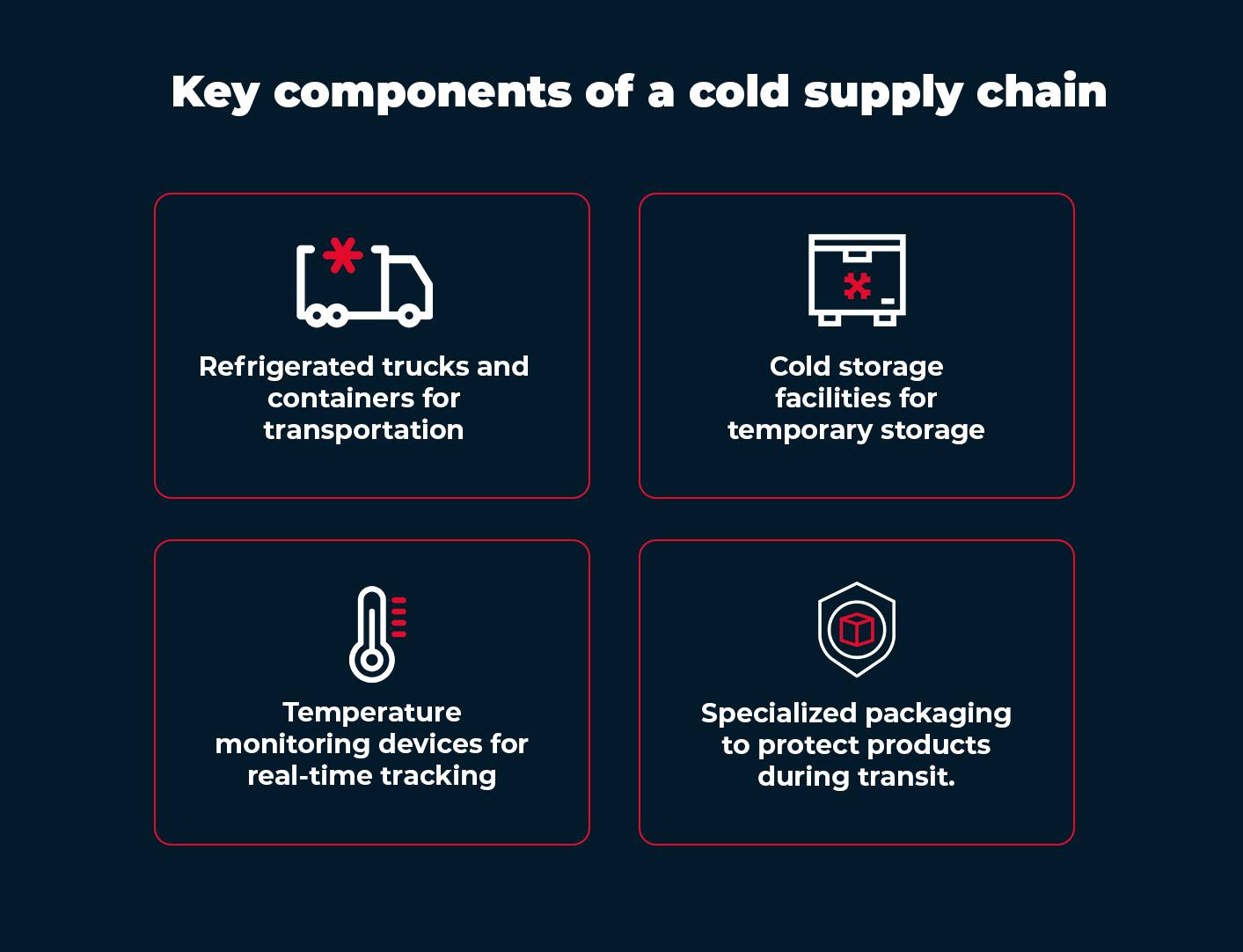
Key Components of the Cold Chain System
A cold supply chain is a complex system comprising various components, such as:
– Refrigerated trucks and containers for transportation.
– Cold storage facilities to store products.
– Temperature monitoring devices for real-time tracking.
– Insulated packaging to safeguard products during transit.
Repercussions of Poor Cold Supply Chain Management
Inadequate cold supply chain management can have severe consequences, including-

How Can TMS Improve Cold Supply Chain Operations?
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) can significantly enhance cold chain operations by optimizing various aspects of the transportation process, ensuring the efficient and reliable delivery of temperature-sensitive goods. Here are some ways TMS can improve cold supply chain operations:

Route Optimization:
TMS software can analyze various factors, such as distance, road conditions, traffic, and weather, to determine the most efficient routes for temperature-controlled shipments. By minimizing transit times and reducing the exposure of products to temperature fluctuations, TMS helps maintain product integrity.
Real-Time Monitoring:
TMS can integrate with temperature monitoring devices and sensors within refrigerated trucks and containers. This integration enables real-time tracking of temperature and location. If temperature deviations occur during transit, TMS can send alerts to logistics personnel, allowing them to take immediate corrective actions to prevent product spoilage.
Visibility and Transparency:
TMS provides end-to-end visibility into the supply chain. It allows stakeholders to track the status of shipments, including estimated arrival times, delays, and any temperature variations. This transparency helps in making informed decisions and ensures that products are handled with care.
Capacity Planning:
TMS can optimize the loading of temperature-sensitive products in vehicles, ensuring efficient utilization of space while maintaining the required temperature conditions. This can lead to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Schedule Planning:
TMS can manage appointment scheduling for loading and unloading, allowing precise coordination between suppliers, carriers, and receivers. Timely appointments reduce wait times, which can be critical for temperature-sensitive goods.
Inventory Management:
TMS helps maintain inventory levels by providing real-time information on the status and location of goods. This is especially important in cold chains where inventory turnover is high, and product shelf life is limited.
Documentation and Compliance:
TMS can assist in automating documentation and compliance requirements, such as generating temperature logs, regulatory reports, and invoices. This reduces the administrative burden and ensures adherence to regulatory standards.
Fleet and Carrier Management:
TMS allows companies to evaluate the performance of their own fleet and carriers. This is done by tracking metrics like on-time delivery, temperature compliance, and overall service quality. The data can be used to make informed decisions regarding supplier and carrier relationships.
Data Integration:
TMS can integrate with other systems, such as warehouse management systems (WMS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, and inventory management systems. This integration streamlines data flow and improves the accuracy of information across the supply chain.
Cost Efficiency:
By optimizing routes, reducing fuel consumption, and minimizing product losses due to temperature deviations, TMS contributes to overall cost savings in the cold supply chain.
Ignite Your Journey Towards Cold Supply Chain Excellence
Cold supply chain logistics is a complex yet crucial element of various industries. It ensures that temperature-sensitive products reach consumers in the best possible condition. With efficient management, monitoring solutions, and technology, the cold supply chain becomes a powerful ally in preserving product quality and safety. Click the red button below to know more Supply Chain Visibility Software.
92





@LogiNext