
The Rise of Quick Commerce in Urban Areas
In recent years, quick commerce (q-commerce) has transformed the way urban populations shop and receive goods. As consumer expectations shift towards faster and more efficient delivery services, businesses are adopting innovative strategies to meet these demands. Central to this transformation is the role of last mile delivery software. This ensures seamless and speedy delivery operations in densely populated urban areas.
What is Quick Commerce?
Quick commerce refers to the rapid delivery of goods, typically within 30 mins to a few hours. Unlike traditional e-commerce, which might fulfill orders in days, q-commerce focuses on ultra-fast deliveries. It caters to essential items like groceries, medicines, and ready-to-eat meals. Urban areas, with their high population density and digital penetration, provide the perfect environment for this industry to flourish.
The Role of Technology in Q-Commerce
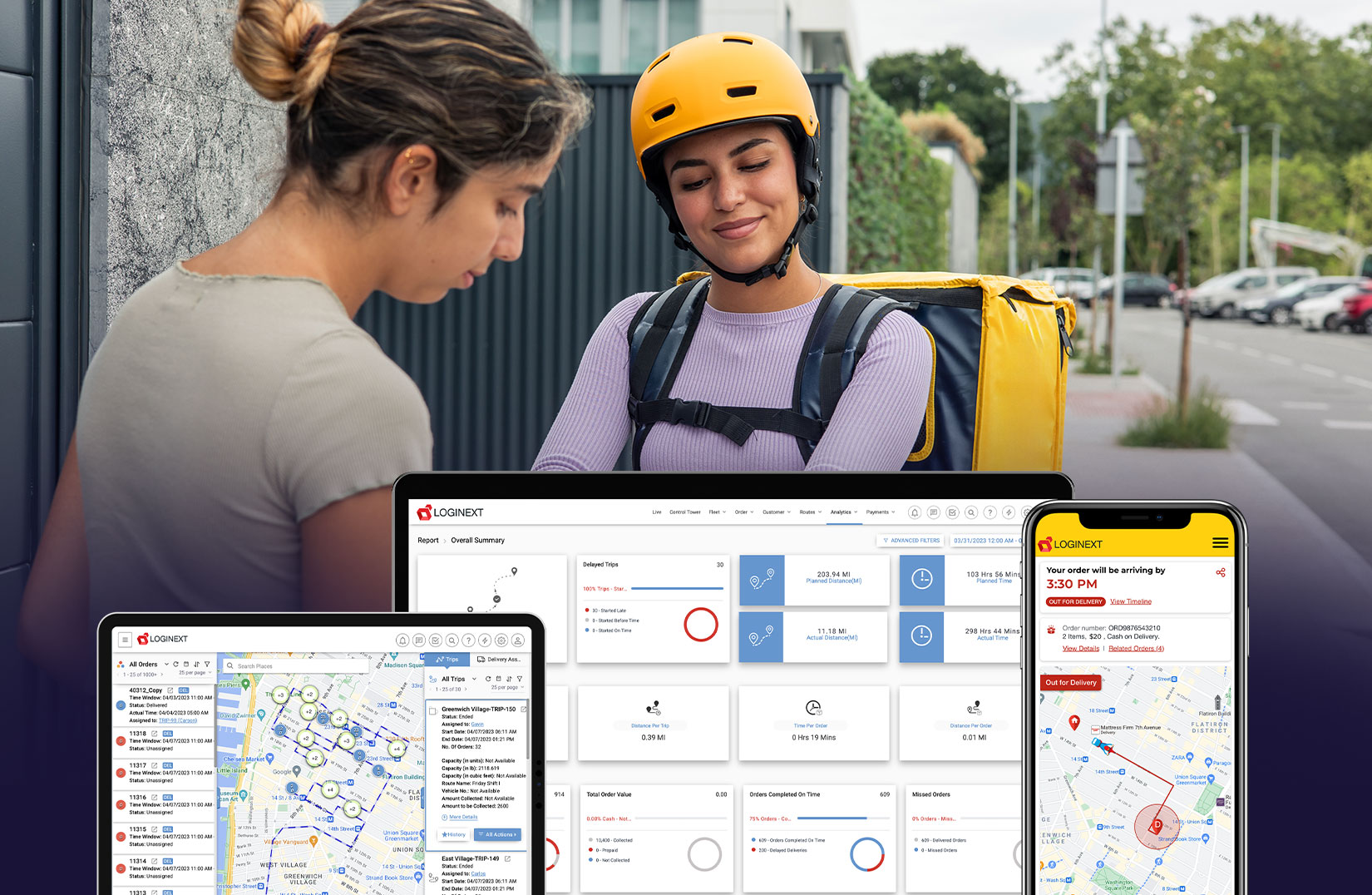
Technology forms the backbone of quick commerce. Advanced last mile delivery systems enable businesses to efficiently handle the complexities of urban logistics. These systems optimize delivery routes, allocate resources effectively and provide real-time updates to customers.
For example, last mile delivery tracking software helps businesses and consumers monitor packages from dispatch to doorstep. Such transparency not only boosts customer satisfaction but also minimizes delays and errors. Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning enhances route optimization, reduces fuel consumption and ensures faster deliveries.
Key Drivers of Quick Commerce Growth

Several factors contribute to the rapid growth of q-commerce:
1. Urbanization:
By 2030, over 60% of the world’s population is expected to live in urban areas. This shift will drive the need for faster and more reliable delivery systems. Urbanization also increases population density, which enhances the feasibility of quick commerce by reducing travel distances for deliveries.
2. Consumer Expectations:
Modern consumers demand convenience and speed. A study by McKinsey found that 75% of shoppers are willing to pay a premium for same-day or instant delivery. Such expectations push businesses to implement the last mile delivery software to remain competitive.
3. Technological Advancements:
The growth of smartphones, GPS, and IoT devices enables businesses to offer real-time tracking and instant updates. This integration reduces uncertainty and boosts consumer confidence in the delivery process.
4. Evolving Retail Models:
Dark stores, which are mini-warehouses located strategically within cities, allow businesses to stock high-demand items close to consumers. This proximity ensures faster deliveries and supports the growth of q-commerce.
5. Market Growth:
The quick commerce market is set to grow from $25 billion in 2021 to $72 billion by 2025, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27%. This growth is fueled by increased internet penetration, higher disposable incomes, and a surge in online shopping trends.
6. Sustainability Trends:
Eco-conscious consumers are encouraging businesses to adopt sustainable delivery practices. Electric vehicles and bike couriers are increasingly used to meet environmental goals while maintaining efficiency in quick commerce operations.
Challenges in Quick Commerce

Despite its advantages, quick commerce faces several challenges:
1. Traffic Congestion:
Urban areas are notorious for traffic congestion, which can significantly delay deliveries. For quick commerce to succeed, businesses must invest in advanced last mile delivery solutions that use AI to optimize routes and minimize delays caused by urban traffic.
2. Cost Pressures:
Ultra-fast deliveries often incur higher operational costs due to the need for additional labor, vehicles, and resources. Last-mile logistics alone contribute to over 50% of total supply chain expenses. Balancing speed with affordability remains a critical challenge for businesses.
3. Sustainability Concerns:
The rapid increase in delivery demands has led to environmental issues, including higher carbon emissions and excessive packaging waste. The transportation sector contributes approximately 20% of global CO2 emissions, with last-mile deliveries being a significant contributor. Companies must adopt eco-friendly practices, such as using electric vehicles or bikes, to address these concerns.
4. Workforce Challenges:
Quick commerce relies heavily on delivery personnel, who often face challenging working conditions, long hours, and high turnover rates. Retaining a motivated and skilled workforce is essential to maintaining service quality.
5. Scalability Issues:
As demand for q-commerce grows, businesses face difficulties in scaling operations without compromising efficiency. Expanding delivery networks and maintaining technological infrastructure requires significant investment and strategic planning.
To overcome these challenges, companies are leveraging innovations such as autonomous delivery vehicles, drone technology, and AI-driven last mile delivery systems. These solutions not only improve operational efficiency but also address sustainability and scalability concerns. Thereby, ensuring the long-term success of quick commerce.
Real-World Success Stories
Several companies have successfully adopted q-commerce models by utilizing cutting-edge last mile delivery solutions:
– Gorillas: This Germany-based startup promises grocery deliveries within 10 minutes using strategically located micro-fulfillment centers.
– Instacart: Operating in North America, Instacart’s same-day grocery delivery service relies heavily on last mile delivery software to optimize operations.
– Zomato & Swiggy: In India, these food delivery giants use advanced tracking systems to ensure prompt deliveries and high customer satisfaction. Notably, Zomato reported a 30% improvement in delivery efficiency after integrating AI-driven last mile delivery tracking software.
The Future of Quick Commerce
As the quick commerce sector continues to expand, the importance of last mile delivery software cannot be overstated. Emerging trends like autonomous vehicles, drone deliveries, and AI-driven analytics will further revolutionize urban logistics. By 2030, it is expected that over 80% of quick commerce deliveries will incorporate some form of automation.
For businesses, investing in the best last mile delivery software is not just a necessity but a strategic move to stay ahead in a competitive market. As technology evolves, so too will the possibilities for delivering goods faster, cheaper, and more sustainably.
Conclusion
Quick commerce is reshaping urban retail landscapes, driven by the demand for speed, convenience, and reliability. The integration of advanced last mile delivery systems is key to overcoming the challenges of urban logistics. With innovations in last-mile delivery tracking software and sustainable solutions, businesses can meet consumer expectations. At the same time, they can pave the way for a more efficient and eco-friendly future.
In the fast-paced world of urban commerce, the ability to deliver on time is a game-changer. For businesses looking to thrive, adopting a robust last mile delivery solution Like LogiNext Mile is not optional – it is essential. Click on the red button below and book a demo with LogiNext today.
76





@LogiNext